Appearance
文件系统
实际上就是建立了一些组织结构, 包括系统引导区, 目录和文件
在使用之前需要进行格式, 格式化会建立文件按分配表等
磁盘分区表: 把一块磁盘划分多个分区
在存储文件的时候会创建文件索引, 指明文件存放的物理地址, 之后把文件存储
实际结构:
- 文件分配表
在文件不是连续的时候只有目录不够用, 记录了文件的位置, 以及下一个扇区的位置
- 目录
记录文件的开始簇, 大小, 日期, 属性等
- 应用
Fatfs
使用C语言的文件操作函数

fatfs是一个面向嵌入式的小型文件系统, 完全使用C语言, 独立于底层的I/O介质
支持Fat12, Fat16, Fat32
FatFs - Generic FAT Filesystem Module (elm-chan.org)
不能开代理
- doc: 帮助文档
- src: 源码
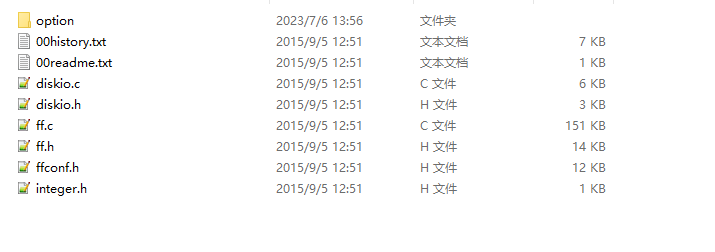
history: 文件版本信息
readme: 帮助信息
integer.h 变量的定义
diskio.c: 底层操作函数, 需要自己实现
ff.c核心文件, 实现管理方法, 文件系统和底层的转换, 根据配置实现函数
ffconfig.h, 配置文件, 包含了各种宏定义, 用于裁剪, 支持的语言
option: 支持的语言编码
实际实现
首先添加所有src文件
之后包含头文件路径
由于这是一个示例文件, 所以有的头文件不存在
diskio.h
c
DWORD get_fattime(void)
{
return 0;
}缺少函数, 手动添加
实际实现函数
- disk_initialize初始化函数
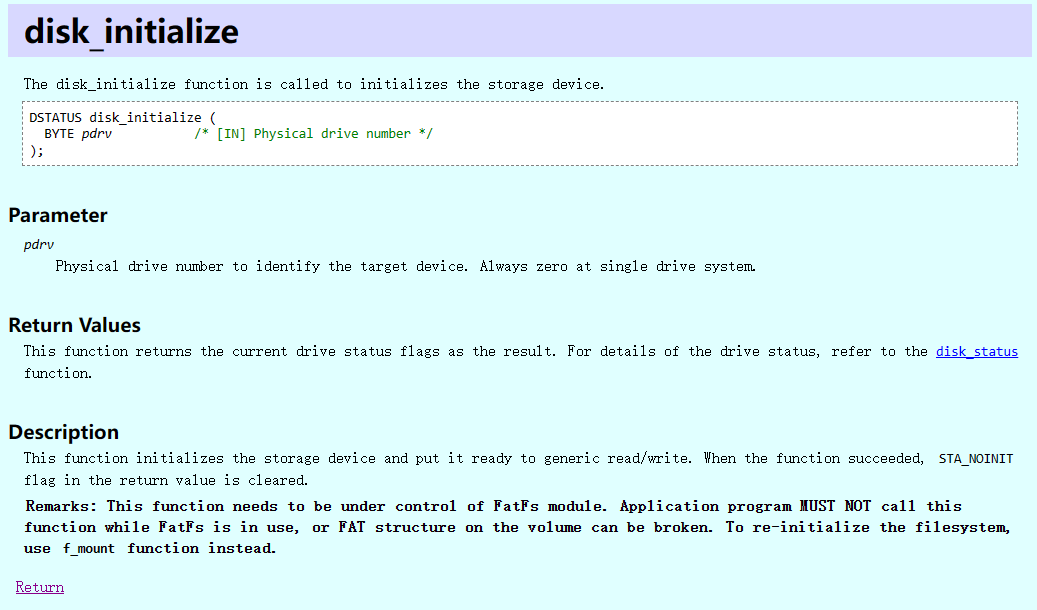
初始化函数, 使得存储器可读可写, 返回值把STA_NOINIT清零, 参数是初始化的内存编号
在使用的时候用上层函数, f_moun
c
DSTATUS disk_initialize (
BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{
DSTATUS stat;
switch (pdrv) {
case SD_CARD :
return stat;
case SPI_FLASH :
SPI_FLASH_Init();//初始化
SPI_Flash_WAKEUP();//唤醒
//直接调用状态函数
return disk_status(pdrv);
}
return STA_NOINIT;
}- disk_status
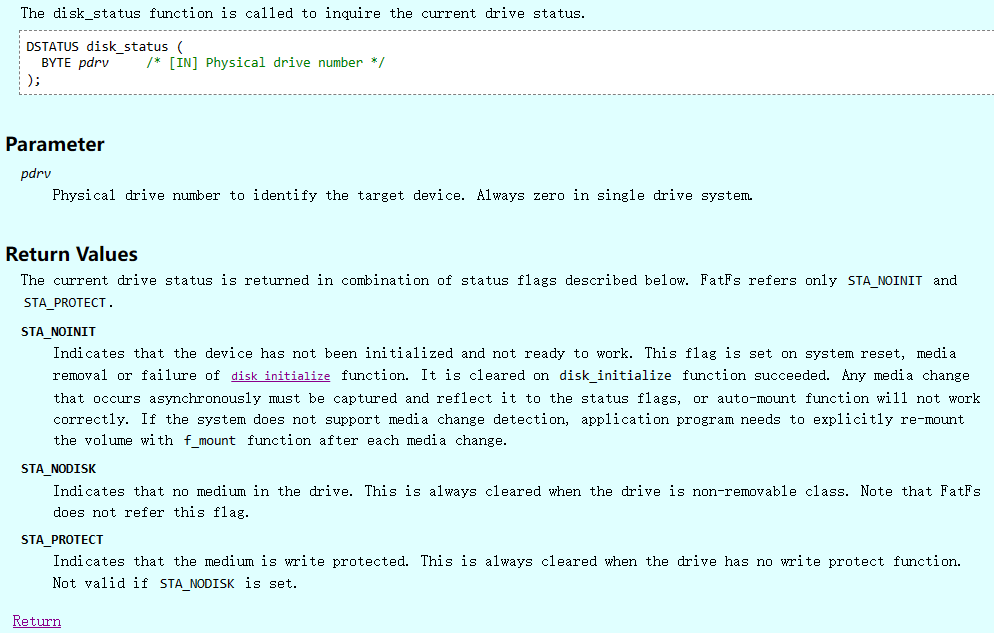
初始化正常返回0, 否则返回上面的值
c
DSTATUS disk_status (
BYTE pdrv /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
)
{
DSTATUS stat;
//int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case SD_CARD :
return stat;
case SPI_FLASH :
if(SPI_FLASH_ReadID() == sFLASH_ID)
{
//正常
stat = 0;
}else
{
//不正常
stat = STA_NOINIT;
}
return stat;
}
return STA_NOINIT;
}- disk_read
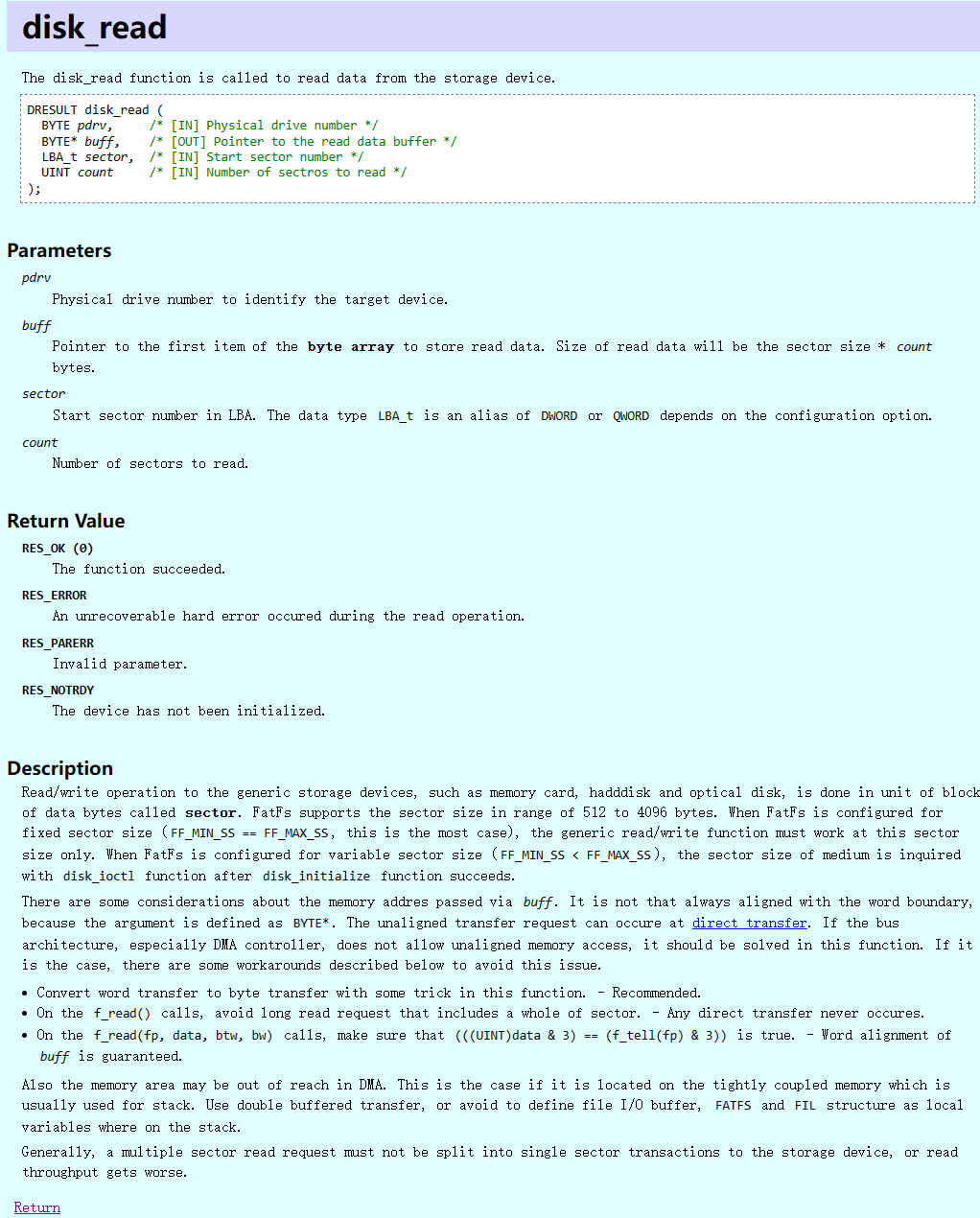
返回值是一个枚举类型
c
DRESULT disk_read (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
BYTE *buff, /* Data buffer to store read data */
DWORD sector, /* Sector address in LBA */
UINT count /* Number of sectors to read */
)
{
DRESULT res;
//int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case SD_CARD :
return res;
case SPI_FLASH :
//使用扇区作为单位, 所以进行地址转换
SPI_FLASH_BufferRead(buff, (sector * 4096), (count * 4096));
res = RES_OK;
return res;
}
return RES_PARERR;
}- disk_ write
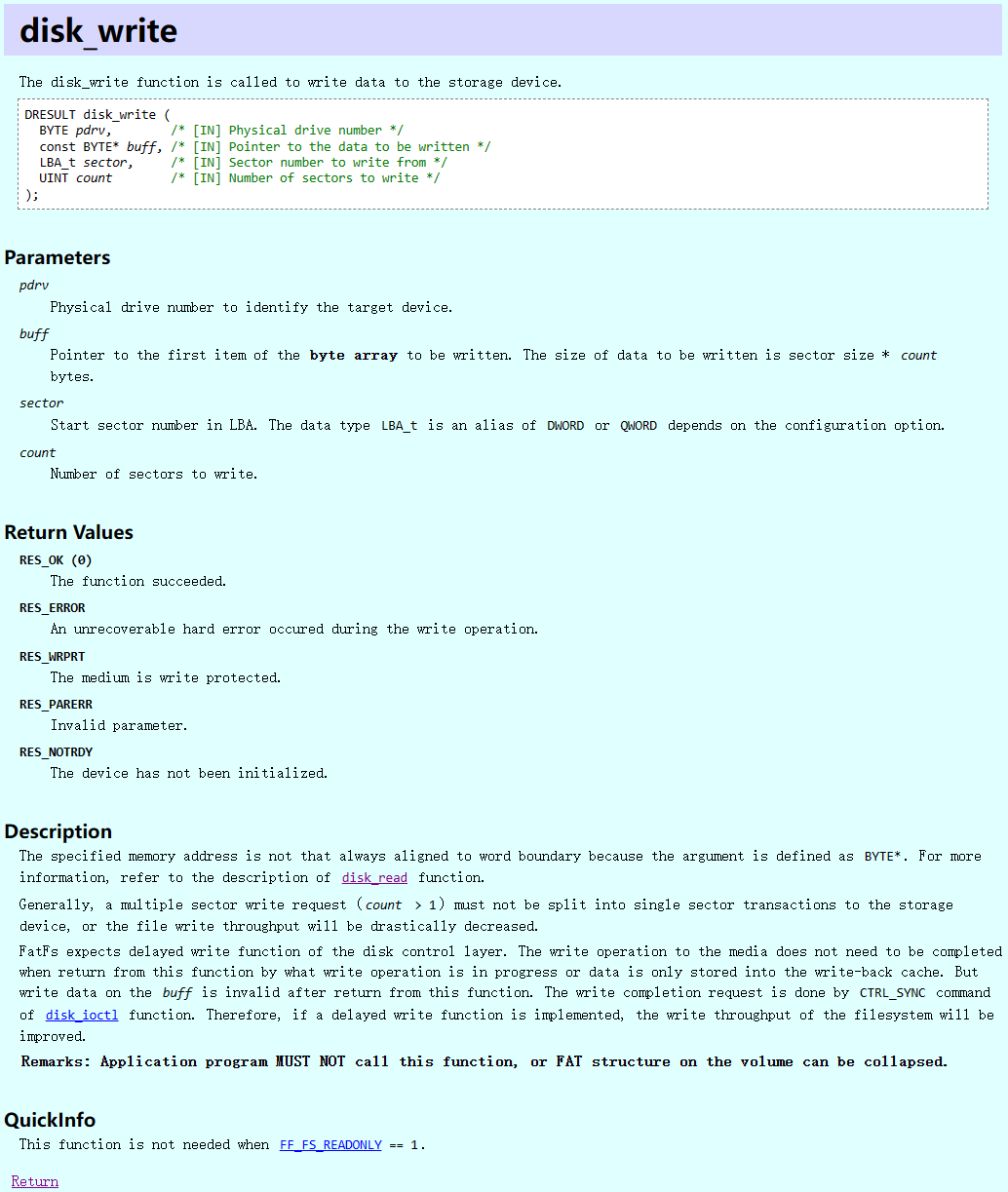
c
DRESULT disk_write (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive */
const BYTE *buff, /* Data to be written */
DWORD sector, /* Sector address in LBA */
UINT count /* Number of sectors to write */
)
{
DRESULT res;
//int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case SD_CARD :
return res;
case SPI_FLASH :
//写入
SPI_FLASH_SectorErase(sector * 4096);
SPI_FLASH_BufferWrite((BYTE *)buff,(sector * 4096), (count * 4096) );
return res;
}
return RES_PARERR;
}- disk_ioctl
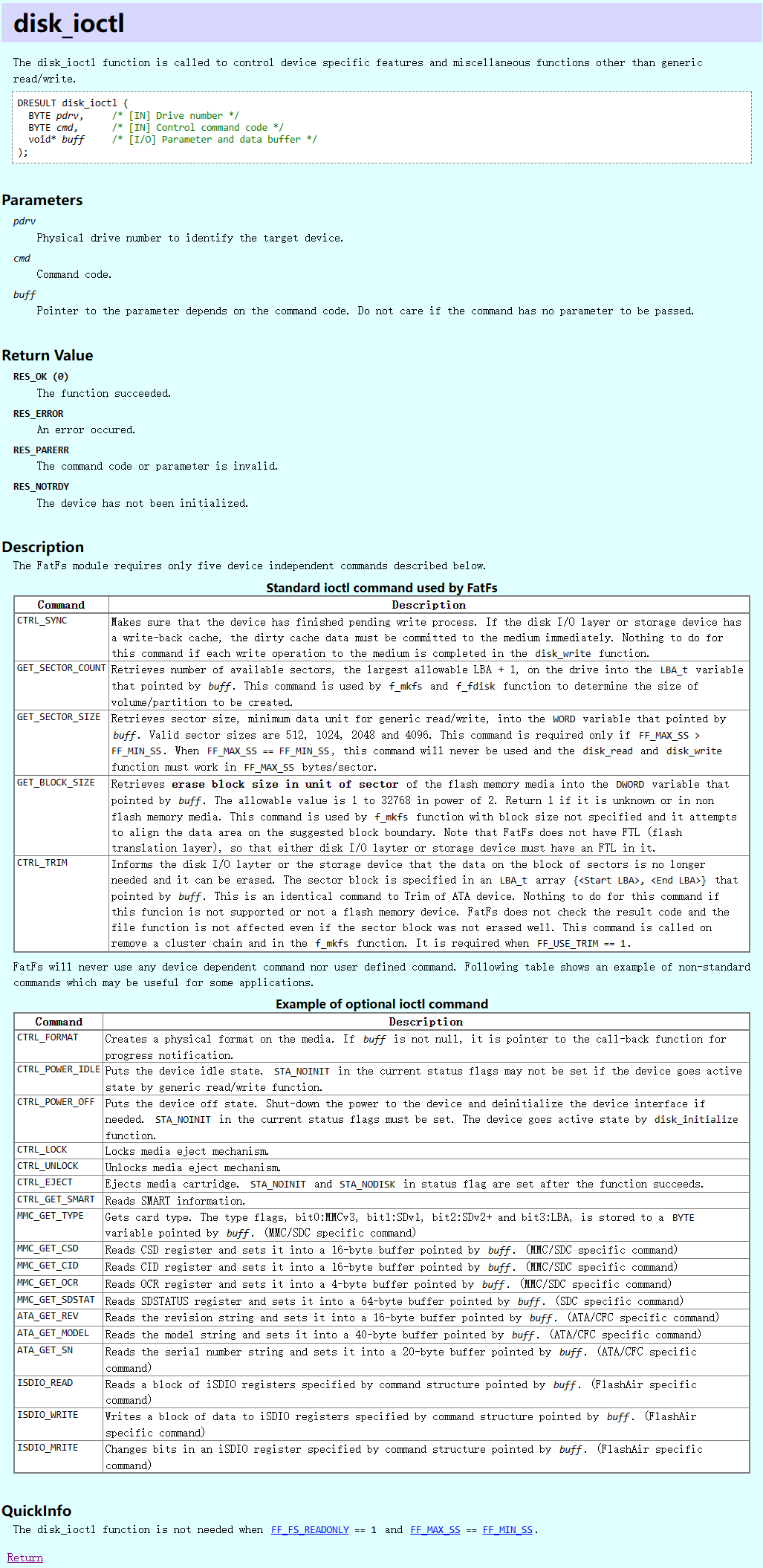
通过命令获取信息, 实现杂项, 用来格式化
- 写入
CTRL_SYNC: 用来确保信息已经写入(又换成的设备需要实现)
- 格式化
GET_SECTOR_COUNT: 获取扇区的多少
GET_BLOCK_SIZE: 每次擦除的块的大小
- 扇区大小不一样
GET_SECTOR_SIZE: 扇区的多少
c
DRESULT disk_ioctl (
BYTE pdrv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE cmd, /* Control code */
void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
{
DRESULT res;
//int result;
switch (pdrv) {
case SD_CARD :
//预留SD卡
return res;
case SPI_FLASH :
//实现命令
switch(cmd)
{
case GET_SECTOR_COUNT:
//拥有的空间, 扇区个数
*(DWORD *)buff = 2048;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_SIZE:
//返回扇区的大小
*(WORD *)buff = 4096;
break;
case GET_BLOCK_SIZE:
//返回擦除扇区的最小个数
*(WORD *)buff = 1;
break;
}
//默认返回值是成功
res = RES_OK;
return res;
}
return RES_PARERR;
}实际使用
- 添加头文件ff.h
- 挂载文件系统, f_mount函数
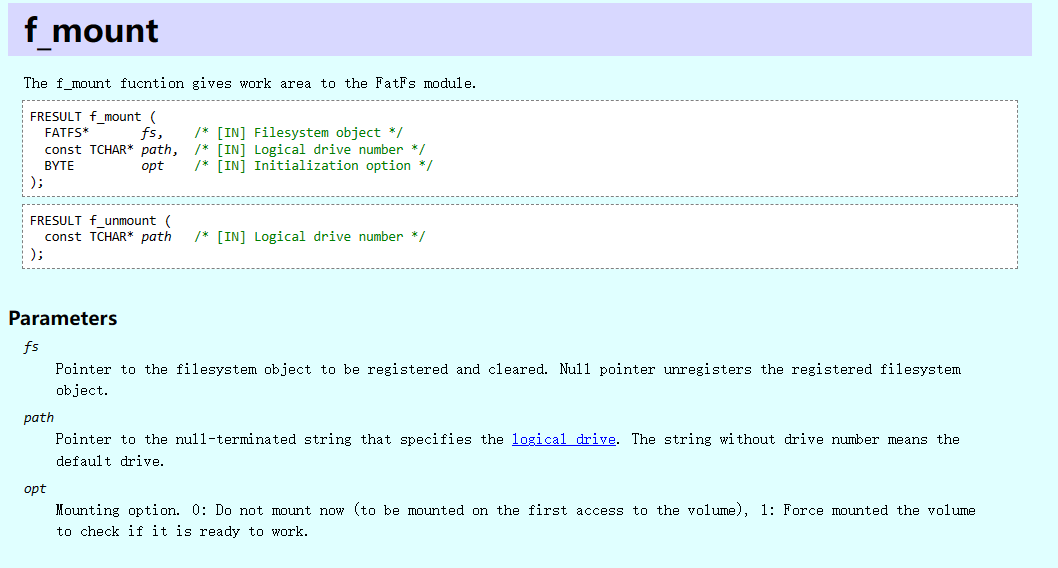
初始化一个FATFS结构体, 占用内存比较大, 定义为全局变量
挂载
c
#include "stm32f10x.h"
#include "bsp_led.h"
#include "bsp_usart.h"
#include "bsp_spi.h"
#include "ff.h"
FATFS fsObject;
int main()
{
//返回值
FRESULT res;
//读取数据缓冲区
USART_Config();
printf("串口初始化完成\n");
//挂载文件系统,初始化Flash, 立即挂载
res = f_mount(&fsObject, "1:", 1);
printf("res = %d", res);
while(1){
}
}这时候返回值为11, 原因是因为默认的设备数是1个
c#define _VOLUMES 1 /* Number of volumes (logical drives) to be used. */
改过之后卡死了, 原因是溢出, 具体是扇区返回值和初始化的值不一样
c#define _MIN_SS 512 #define _MAX_SS 512 /* These options configure the range of sector size to be supported. (512, 1024, / 2048 or 4096) Always set both 512 for most systems, all type of memory cards and / harddisk. But a larger value may be required for on-board flash memory and some / type of optical media. When _MAX_SS is larger than _MIN_SS, FatFs is configured / to variable sector size and GET_SECTOR_SIZE command must be implemented to the / disk_ioctl() function. */最大值改为4096
之后返回13, 原因是没有文件系统
使用函数f_mkfs
c#define _USE_MKFS 0 /* This option switches f_mkfs() function. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */配置为1, 使能格式化
格式化之后需要重新挂载
cif(res==13) { f_mkfs("1:", 0, 0); res = f_mount(NULL, "1:", 1); res = f_mount(&fsObject, "1:", 1); }
c
#include "stm32f10x.h"
#include "bsp_led.h"
#include "bsp_usart.h"
#include "bsp_spi.h"
#include "ff.h"
FATFS fsObject;
FIL fp;
UINT bw;
unsigned char writeData[] = "焦浩洋测试文件\n";
unsigned char readData[1024];
int main()
{
//返回值
FRESULT res;
//读取数据缓冲区
USART_Config();
printf("串口初始化完成\n");
//挂载文件系统,初始化Flash, 立即挂载
res = f_mount(&fsObject, "1:", 1);
printf("res = %d\n", res);\
//没有操作系统进行创建
if(res==13)
{
f_mkfs("1:", 0, 0);
res = f_mount(NULL, "1:", 1);
res = f_mount(&fsObject, "1:", 1);
printf("格式化文件系统\n");
}
//打开文件, 设置打开文件的模式
res = f_open(&fp, "1:jiao.txt", FA_OPEN_ALWAYS| FA_WRITE | FA_READ);
printf("打开文件res = %d\n", res);
if(res == FR_OK)
{
res = f_write(&fp, writeData, sizeof(writeData), &bw);
printf("写文件res = %d, %d\n", res, bw);
if(res==FR_OK)
{
//更改文件指针位置为开头
f_lseek(&fp, 0);
res = f_read(&fp, readData, f_size(&fp), &bw);
if(res == FR_OK)
printf("文件: %s", readData);
}
}
//关闭文件
f_close(&fp);
while(1){
}
}- 支持中文文件名
c
#define _CODE_PAGE 932
/* This option specifies the OEM code page to be used on the target system.
/ Incorrect setting of the code page can cause a file open failure.
/改为936
c
#define _USE_LFN 0
#define _MAX_LFN 255第一个改成大于0的数字
1: 文件名存储在全局变量
2: 局部变量
3: 堆区
错误
在返回值的时候一定要返回规定值
文件系统实际操作
f_getfree: 获取文件系统的剩余空间
f_read: 如果读取的数据少于要求的数字=> 文件比较小, 已经到了结尾
f_unlink: 删除文件
f_stat: 文件信息读取, 会储存长文件名
f_readdir: 获取目录文件信息, 再次调用获取下一个文件
