Appearance
启动过程浅析

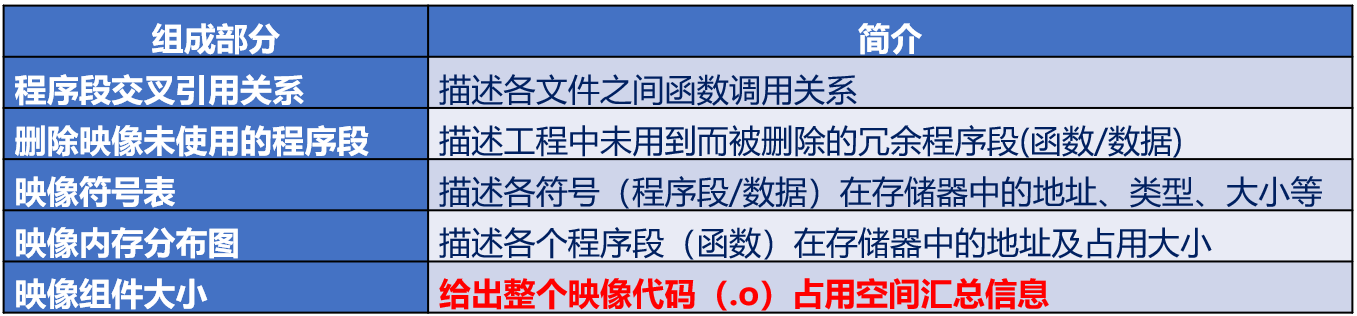
MAP文件
MDK编译以后产生的集程序, 数据以及IO空间的一种映射关系的列表文件
简单地说就是各个c文件, 函数, 符号的地址大小以及引用关系
启动模式
M3/M4/M7等内核复位后,做的第一件事:
1,从地址 0x0000 0000 处取出堆栈指针 MSP 的初始值,该值就是栈顶地址
2,从地址 0x0000 0004 处取出程序计数器指针 PC 的初始值,该值是复位向量
系统复位以后第四个时钟上升沿BOOT引脚的值会被锁存
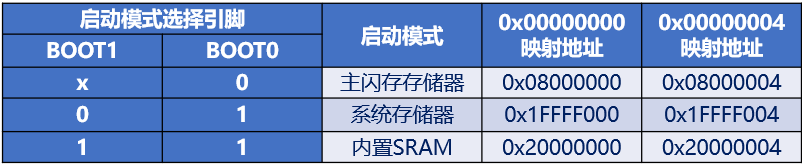
st公司对不同的启动方式进行了不同的映射
主闪存对应的就是我们常用的flash
系统存储器里面有bootloader, 这个是st公司写的, 可以通过USART进行下载程序
内置的SRAM

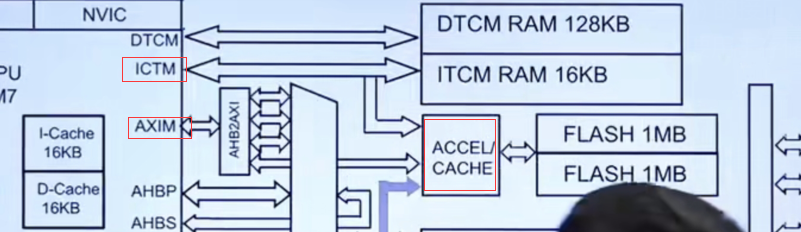
从芯片手册上发现, 使用ITCM和AXIM都可以访问到相同的FLASH
ITCM (Instruction Tightly-Coupled Memory) 是 STM32F7 中的一个片内高速、低延迟、高可靠性的指令存储器区域,它的主要作用是存储常用的程序指令,提高数据读取的效率,降低延迟,提高系统性能。
AXIM (Axi-SRAM Interface) 是片内高速静态随机存储器 (SRAM) 的接口,它与处理器核相连接,可读取或写入处理器的数据。ITCM 和 AXIM 的作用是不同的,ITCM 主要用于存储指令,而 AXIM 主要用于存储数据。这两个区域可以并行访问,提高系统的性能和效率。
为什么要设置为两个而不是一个呢?这是因为处理器需要同时访问指令和数据,并且在访问内存时需要满足一系列的时序和电气规范。将指令和数据存储在不同的存储区域中,可以提高系统并行访问的效率,降低存储器访问之间的竞争,避免数据与指令之间的干扰。此外,通过对不同存储区域进行不同的配置,可以更好地满足不同的应用需求。
从ITCM启动和从AXIM启动的主要区别在于访问速度和访问方式。从ITCM启动的程序可以获得更快的访问速度,因为ITCM位于处理器的指令总线上,读取指令时直接从ITCM中读取,无需通过处理器总线和外部存储器进行访问。从AXIM启动的程序则需要通过处理器总线和外部存储器进行访问,访问速度会较慢。此外,从ITCM启动的程序不能超出ITCM的地址范围,因为ITCM的容量较小,通常只有几十KB到几百KB左右,适用于存储常用的指令。而从AXIM启动的程序则可以访问较大的外部存储器容量。总之,从ITCM启动的程序可以获得更快的访问速度,但存储容量较小,只适用于存储常用的指令;而从AXIM启动的程序则可以访问较大的外部存储器容量,但访问速度较慢。在实际应用中,可以根据具体的需求选择不同的启动方式。
由于设置的位最小的是第14位, 对应的是16KB, 所以设置的最小单位是16KB(实际地址是32位控制的, 但是我们只能设置里面的16位)

允许配置为0x00000000到0x3fff0000, 低16位位只能为0
启动过程
- 内部flash的启动模式
- 获取MSP指针的值0x80000000
- 获取PC指针的值0x80000004
- PC指向的是Reset_Handler, 在启动文件里面
- 启动文件
- 设置MSP
- 初始化PC
- 设置堆栈的大小
- 初始化中断向量表
- 调用初始化函数
- 调用__main
assembly
; Reset handler
Reset_Handler PROC ;定义一个子程序
EXPORT Reset_Handler [WEAK] ;设置为若定义, 可以自己实现一个这个函数
IMPORT __main
IMPORT SystemInit
LDR R0, =SystemInit
BLX R0
LDR R0, =__main
BX R0
ENDP ;子程序结束相当于C语言函数的结束c
void SystemInit (void)
{
#if defined(STM32F100xE) || defined(STM32F101xE) || defined(STM32F101xG) || defined(STM32F103xE) || defined(STM32F103xG)
#ifdef DATA_IN_ExtSRAM
SystemInit_ExtMemCtl();
#endif /* DATA_IN_ExtSRAM */
#endif
/* Configure the Vector Table location -------------------------------------*/
#if defined(USER_VECT_TAB_ADDRESS)
SCB->VTOR = VECT_TAB_BASE_ADDRESS | VECT_TAB_OFFSET; /* Vector Table Relocation in Internal SRAM. */
#endif /* USER_VECT_TAB_ADDRESS */
}__main函数的作用
- __main函数 作用:Initialization of the execution environment and execution of the application
You can customize execution intialization by defining your own __main that branches to __rt_entry.
The entry point of a program is at __main in the C library where library code:
Copies non-root (RO(不会拷贝,官方提供和实际实践有出入) and RW) execution regions from their load addresses to their execution addresses. Also, if any data sections are compressed, they are decompressed from the load address to the execution address. Zeroes ZI regions. Branches to __rt_entry. If you do not want the library to perform these actions, you can define your own __main that branches to __rt_entry.
注意:__main函数不会将RO段数据拷贝到执行地址处,虽然官方说明了
- _rt_entry函数
procedure The library function __rt_entry() runs the program as follows:
Sets up the stack and the heap by one of a number of means that include calling __user_setup_stackheap(), calling __rt_stackheap_init(), or loading the absolute addresses of scatter-loaded regions.
Calls __rt_lib_init() to initialize referenced library functions, initialize the locale and, if necessary, set up argc and argv for main().This function is called immediately after__rt_stackheap_init() and is passed an initial chunk of memory to use as a heap. This function is the standard ARM C library initialization function and it must not be reimplemented.
Calls main(), the user-level root of the application.
From main(), your program might call, among other things, library functions.
Calls exit() with the value returned by main().
entry的是ARM汇编语法中程序的入口地址,GNU Assember语法中start是程序的入口地址
__rt_lib库函数是没有源文件,都已经编译完成了。
The symbol __rt_entry is the starting point for a program using the ARM C library.
Control passes to __rt_entry after all scatter-loaded regions have been relocated to their execution addresses.
- Usage The default implementation of __rt_entry:
Sets up the heap and stack. Initializes the C library by calling __rt_lib_init.(ARMc库里面全面都是.b .l形式的库,没有源码) Calls main(). Shuts down the C library, by calling __rt_lib_shutdown. Exits. __rt_entry must end with a call to one of the following functions:
- exit()
Calls atexit()-registered functions and shuts down the library.
- __rt_exit()
Shuts down the library but does not call atexit() functions.
- _sys_exit()
Exits directly to the execution environment. It does not shut down the library and does not call atexit() functions.